CLAUD-IT, the EU’s multidisciplinary project aimed at improving clinical audit practices, has developed its first clinical audit guideline for nuclear medicine: NuCline.
In a EuroSafe 2025 poster, a team headed by Prof. Dr. Roman Klöckner, head of the Institute of Interventional Radiology at the Clinic of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine at the University of Lübeck, Germany outlined NuCline in the context of the CLAUD-IT project.
CLAUD-IT was built in part on the QuADRANT and EU-JUST-CT projects, using resources developed by the European Society of Radiology and the European Association of Nuclear Medicine, to improve the overall quality and safety of radiology and nuclear medicine procedures through justification and optimization.
The project is developing a training program for auditors, including guidelines and supporting documents. All CLAUD-IT materials will be made available through a free access repository.
After consideration of recent initiatives and infrastructure, as well as a needs assessment, CLAUD-IT has developed NuCline, its first nuclear medicine guide. NuCline is a comprehensive guide for clinical audits performed in nuclear medicine, intended to support best practices and comply with regulatory frameworks.
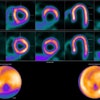
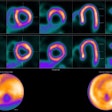
 Audit cycle in nuclear medicine.Prof. Dr. Roman Klöckner et al and presented at EuroSafe 2025.
Audit cycle in nuclear medicine.Prof. Dr. Roman Klöckner et al and presented at EuroSafe 2025.
NuCline includes a number of audit templates divided into four topics: clinical audit, regulatory audit, radiopharmacy, and quality control for equipment.
Additionally, the existing ESPERANTO – ESR Guide to Clinical Audit in Radiology has been updated and expanded for the project to create AUDITRAD: Esperanto – Guide to Clinical Audit in Radiology. The guide’s audit templates have been revised and updated according to current standards and regulations, and 33 templates have been added. The new templates cover topics such as radiation protection and AI tools.
An Implementation Board for the CLAUD-IT project has been set up, comprising national implementation teams from the nine EU countries participating in the CLAUD-IT pilot campaigns (Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Germany, Greece, Italy, Romania, Slovenia, and Spain).
The implementation teams include representatives from national radiology and nuclear medicine societies and authorities or agencies responsible for clinical audits.
The Implementation Board’s goal is to plan the wider roll-out of clinical audit campaigns and provide support, as well as “to ensure that clinical audit is embedded as a core element of the wider healthcare system,” Klöckner et al explained.
During the pilot CLAUD-IT program, clinical audits will be carried out in two rounds in the participating countries: in the first round, the 11 hospitals included in the consortium will conduct clinical audits in radiology and nuclear medicine; the second round will occur after feedback and data are analyzed from the first round and adjustments are made. These second-round audits will be performed at three to six additional recruited hospitals per country.
The EuroSafe poster may be read here; more information about the CLAUD-IT initiative is available on the ESR website.