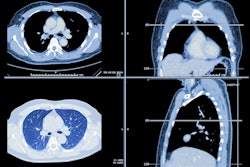
Serac Healthcare and the University of Exeter are highlighting findings for the novel SPECT imaging agent technetium-99m (Tc-99m) maraciclatide as an imaging marker for interstitial lung disease evaluation.
Researchers presented data from the study at the European Respiratory Society conference taking place from 27 September to 1 October in Amsterdam.
The initial findings show the feasibility of using Tc-99m maraciclatide to evaluate disease activity. The findings are part of a sub-study of the PRospective Evaluation of Interstitial Lung Disease progression with quantitative CT (PREDICT-ILD) phase II clinical trial.
The university is leading research efforts, with the sub-study including 10 patients and five healthy controls. The findings include increased activity in patients with interstitial lung disease compared to healthy controls and feasible visualization of inflammation in patients. The researchers also found that whole lung uptake of the imaging marker was greatest in those with fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis.