A new artificial intelligence (AI) tool can accurately detect coronary CT angiography (CCTA) images of the arteries with significant stenoses, flagging them for priority reading by a human expert in a few seconds, a French expert has reported.
The deep-learning model (DLM) "Coronary-Expert," optimizes workflow and allows doctors to act faster to treat sicker patients first by helping them prioritize analysis of images.
The model, which uses multiple curved multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) CCTA images of the three main coronary arteries from nine angles around the 360° arterial circumference, can differentiate normal, nonobstructive, and obstructive arteries with similar performance to a trained radiologist, noted Dr. Jean-François Paul, head of cardiac imaging at the Institut Mutualiste Montsouris in Paris and founder and CEO of Spimed-AI.
"It's like having another experienced set of eyes. The main effects are confidence and reduced mental charge for radiologists as there is less risk of error, and time-saving, which alters the workflow drastically as the technician can prepare the case and alert the radiologist when the system shows a red flag for significant stenosis," he told AuntMinnieEurope.com.
How deep learning works
The technician performs cMPR extraction, and images are automatically sent from the reconstruction software to Coronary-Expert, via the Cloud or a local Server.
The DLM categorizes images into three categories following the Coronary Artery Disease Reporting and Data System (CAD-RADS). CAD-RADS 0 is normal and flagged green; CAD-RADS 1 and 2 are for stenoses under 50%, flagged orange; and CAD-RADS 3 to 5 indicate over 50% stenosis and are flagged red.
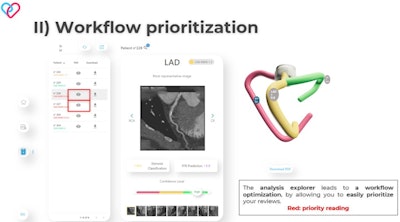 In the Coronary-Expert interface, the "analysis explorer" allows doctors to optimize their reading workflow, by prioritizing red cases first.
In the Coronary-Expert interface, the "analysis explorer" allows doctors to optimize their reading workflow, by prioritizing red cases first.Results are computed and a PDF report is generated and available onsite in less than 30 seconds. In the case of a severe stenosis -- a red case -- the physician is automatically alerted by email. In the Coronary-Expert interface, the "analysis explorer" allows doctors to optimize their reading workflow by prioritizing red cases first.
Risk reduction
Paul, who co-authored a paper evaluating Coronary-Expert published online in Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging on 25 January, outlined the expert level accuracy of the DLM. This high accuracy allows workflow improvements to reduce the risk of patient discharge before interpretation and accelerate the patient's care pathway. It also leaves more time available for difficult cases and clinical time with patients.
On an outpatient basis, around 15% of patients have a stenosis of at least 50%. Of these, 85% are considered normal or not significantly stenotic at CAD-RADS 0-2. If experts are used for just these 15% of stenosis cases, with technicians managing the rest, 30% to 40% of outpatient interpretation and reporting time can be saved, according to Paul.
"Accuracy was excellent for differentiating patients with vs. without stenoses ≥ 50%. The high negative predictive value of 97% at the patient level strongly suggests a major role for the DLM to automatically detect images requiring priority CCTA reading," Paul and colleagues stated.
Future steps
The neural network tool which is in the process of being commercialized by Paul's two-year-old startup, Spimed-AI, continues to develop, with new data added from its use in clinical practice across five centers to date, leading to refinement of its accuracy. The corrections work in both directions, with the AI spotting abnormalities missed by the human and the expert tweaking the AI. The plan is for up to 20 centers to feed the model by the end of the year, all of which will be using it as their first line of detection for stable chest pain patients.
"AI allows humans to reach expert level. It is estimated that it takes eight years to become an expert in this field, but after four years of development Coronary-Expert can detect stenoses of 50% and more through just one exam," Paul said.
Given that there are not many experts in coronary CT, the DLM can be used for training purposes, as it provides explanation and shows where the AI found the abnormality or stenosis, he added. In the U.K., for example, there is a shortfall of CT machines so training is limited, he continued, meaning that there is a severe brake on the expansion of CT expertise, and that's where this tool can come to the fore.
Currently, the service is web-based with access to the cloud with a personal code. On-premises solutions are also possible. Licenses for the service are issued per CT scanner. A new website will be up and running in September as will automatic alerts sent to mobile phones for red cases, Paul noted. He also pointed to a new AI tool in Spimed-AI's pipeline based on fractional flow reserve prediction to detect ischemic coronary artery disease and manage treatment by streaming patients to either medication or interventional radiology with stent or bypass.
For the moment though, the focus is on rolling out Coronary-Expert through partnerships with the bigger companies for a three-pronged effect: getting more radiologists involved for purposes of education, increasing training in the field with the tool to help avoid mistakes and accelerate daily workflow, and improving the tool for better patient management.