A leading European MR expert has stressed that late gadolinium enhancement imaging of the nonischemic heart continues to show promise in differential diagnosis, both as a prognostic outcome predictor when disease is already established and as a guide to therapeutic decisions.
Late gadolinium enhancement can be used for diagnosis in cases that can't be solved by echocardiography alone, particularly for differential diagnoses in subtle abnormalities, when a patient is genetically positive but with normal cardiograms, Dr. Daniel Theisen, section chief for MRI at the Grosshadern Clinic, University Hospital of Munich in Germany, told attendees at the recent International Symposium on State-of-the-Art Imaging (iSi 2011) in Bordeaux, France.
"We see a lot of patients where the disease is already clear and we do late enhancement for prediction of outcome. This helps in therapeutic decisions, such as when to perform ICD [implantable cardioverter defibrillator] implantation or resynchronization therapy. Which patients' heart function will be improved by ICD implantation, or cardiac resynchronization therapy, needs to be the focus of further large studies on the detection of diffuse early-onset fibrosis with MRI," he noted.
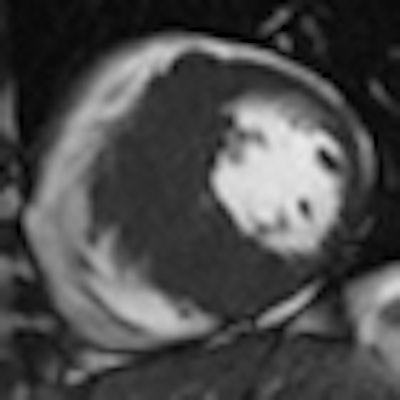
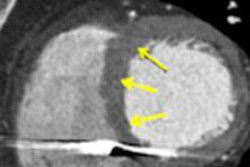
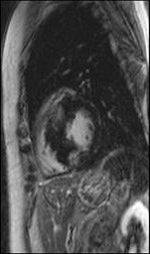 Late gadolinium enhancement shows focal myocardial fibrosis. All images courtesy of Dr. Daniel Theisen.
Late gadolinium enhancement shows focal myocardial fibrosis. All images courtesy of Dr. Daniel Theisen.Late gadolinium enhancement's prognostic capacity for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a cause of sudden death in young athletes, is significant. Citing last year's study by Dr. Rory O'Hanlon, of London's Royal Brompton and Harefield NHS Foundation Trust (Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 7 September 2010, Vol. 56:11, pp. 867-874), Theisen explained that the 217 patients were divided into two groups: those showing late gadolinium enhancement and those not. Patients in the former group were more likely to reach the primary end point of sudden cardiac death and sustain ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. Thus, focal myocardial fibrosis detected by late gadolinium enhancement has proved to be an independent predictor of adverse outcome.
"It is not entirely clear whether these patients with focal myocardial fibrosis in late gadolinium enhancement will benefit from early antifibrotic therapy or ICD implantation in the future," he said.
Absence of large multicenter trials to assess which sequences are best for diagnosing myocarditis means that, for the moment, radiologists must rely on expert consensus papers, some of which have involved T2-weighted MRI, with early or late gadolinium enhancement. As a preventive move, patients showing late gadolinium enhancement on MRI may be prospectively fitted with ICD devices in the future to reduce the risk of arrhythmic events.
Nonischemic heart disease covers a highly heterogeneous group of diseases, Theisen explained. Most nonischemic heart disease patients present with acute onset heart failure. Its incidence is high, with 500,000 new cases per year in the U.S. alone, and it is the leading cause of hospitalization among the elderly.
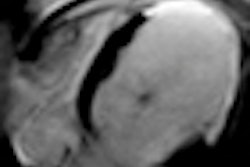
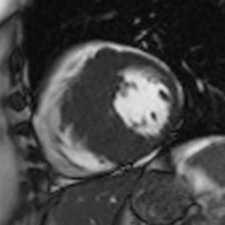 Cine MRI in short axis orientation in a patient with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Cine MRI in short axis orientation in a patient with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.In workup, radiologists need to assess functional parameters to discover the extent of deterioration and its underlying pathological conditions, as well as assess myocardial status of the left ventricle in terms of whether the changes can be reversed or not. There are plenty of tools in the doctors' toolbox, including flow measurements, cine MRI, stress and rest perfusion, MR angiography, and high-resolution T1- and T2-weighted morphological imaging of both ventricles. In addition, images acquired 10 to 30 minutes after gadolinium administration can show typical though not specific patterns that help the radiologist to narrow the differential diagnosis in case of heart failure of unknown etiology.
Late gadolinium enhancement "can show the difference between ischemic and nonischemic heart conditions, can narrow the differential diagnoses in nonischemic hearts by 'typical' patterns, and can guide biopsy procedures by detecting focal areas of myocardial fibrosis. Furthermore, it helps phenotyping genetically positive patients as a supplement to echocardiography," he concluded.