Swedish researchers have found that digital tomosynthesis complements radiography and CT for the monitoring of patients with cystic fibrosis because the technique has a lower radiation dose than CT exams, and gives a superior visualization of pulmonary cystic fibrosis changes compared with x-rays.
Patients with cystic fibrosis have a life expectancy of 40 to 50 years, during which they undergo frequent chest imaging exams. Because of the longer life expectancy of these patients, performing low-dose exams is very important, especially for pediatric patients.
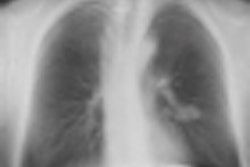
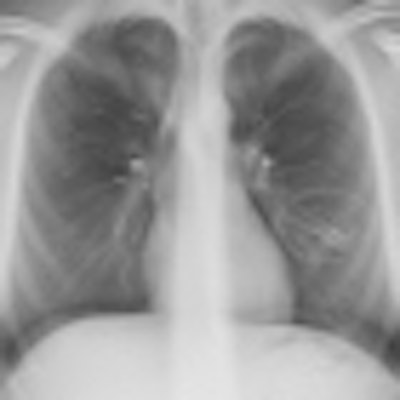
 The anteroposterior (AP) chest x-ray, which is automatically included in the examination, shows increased linear markings in the right upper lobe and small parenchymal changes in the left lung, lateral to the heart. All images courtesy of Dr. Kristina Vult von Steyern.
The anteroposterior (AP) chest x-ray, which is automatically included in the examination, shows increased linear markings in the right upper lobe and small parenchymal changes in the left lung, lateral to the heart. All images courtesy of Dr. Kristina Vult von Steyern.In an article published online on 11 November by Insights into Imaging, Dr. Kristina Vult von Steyern, a pediatric radiologist at Skäne University Hospital's Center for Medical Imaging and Physiology in Lund, Sweden, and colleagues described their experiences using digital tomosynthesis imaging with a patient population of 39 adults ages 19 to 59 years and 36 children ages 8 to 18 years. All were participants of a clinical study of cystic fibrosis patients.
The tomosynthesis images were acquired using the same x-ray system as chest radiography (Definium 8000 and VolumeRAD, GE Healthcare), taking approximately 60 seconds longer than the time to perform a chest x-ray exam. Adults and children older than age 12 were imaged while standing, with patients asked to hold their breath for 10 seconds. To reduce motion artifacts, children between the ages of 8 and 12 were imaged in a supine position. Those younger than age 8 have proved to be unreliable with respect to holding still and holding their breath, and for this reason are excluded from tomosynthesis imaging.
Approximately 60 coronal sectional images with a 3-mm thickness for pediatric patients and a 4-mm thickness for adult patients were acquired. The effective dose was approximately 0.08 mSv for children and 0.12 mSv for adults. By comparison, a typical CT scan can expose a patient up to 10 times the effective radiation dose.
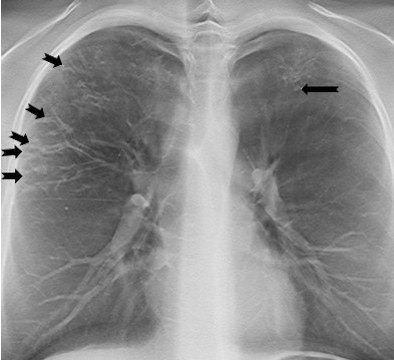 On a tomosynthesis section, cylindrical bronchiectases in the right upper lobe and small mucus plugs in a tree-in-bud pattern in the periphery of the lobe (arrows) are seen, but are not apparent on the AP radiograph. In the apical part of the left upper lobe, small cylindrical bronchiectases and mucus plugs (arrow) are seen.
On a tomosynthesis section, cylindrical bronchiectases in the right upper lobe and small mucus plugs in a tree-in-bud pattern in the periphery of the lobe (arrows) are seen, but are not apparent on the AP radiograph. In the apical part of the left upper lobe, small cylindrical bronchiectases and mucus plugs (arrow) are seen.While typical pulmonary changes in cystic fibrosis such as mucus plugging, bronchial wall thickening, and bronchiectases are superior in tomosynthesis images compared with a chest radiography, they are not superior to images produced by a CT scan. Depth resolution is inferior, and objects such as intravenous lines, tubes, or other devices generate artifacts within the area that is the most distant from the tomosynthesis sections. As a result, the lung parenchyma may be obscured. Localized air trapping and mosaic pattern cannot be adequately evaluated with tomosynthesis.
However, digital tomosynthesis imaging may eliminate the need to perform a CT scan after a chest x-ray for patients, according to the authors. It also provides a much more cost-effective alternative. At Skäne University Hospital, the cost of an anteroposterior (AP) digital radiograph is 48 euros ($62 U.S.) by itself, and a tomosynthesis chest exam is equivalent to 54 euros ($70 U.S.). By comparison, the cost of a chest CT ranges from 161 euros to 214 euros ($209 to $278 U.S.).
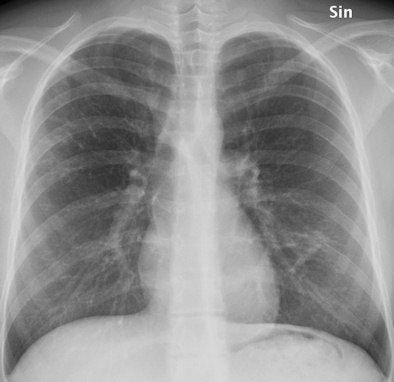
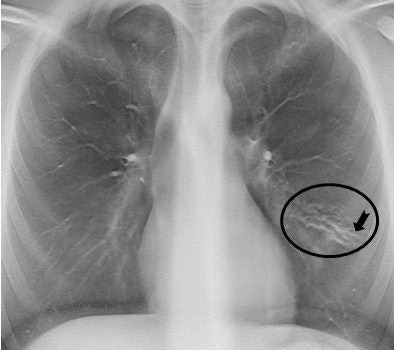 Another tomosynthesis section shows a slightly varicose bronchiectasis with severe wall thickening (circle) in the lingula segment of the left upper lobe. Small mucus plugs are seen in the area (arrow).
Another tomosynthesis section shows a slightly varicose bronchiectasis with severe wall thickening (circle) in the lingula segment of the left upper lobe. Small mucus plugs are seen in the area (arrow).Noting that their image analysis was limited to 145 examinations, the authors recommended that further evaluation of the role of tomosynthesis for monitoring disease progression in both adult and pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis should be undertaken.
Vult von Steyern told AuntMinnieEurope.com that she and her colleagues are planning to formally compare images from tomosynthesis with those of CT images acquired from patients with cystic fibrosis. The objective of this study will be to try to establish indications that determine when it is most appropriate to perform tomosynthesis or CT in follow-up of these patients.