Digital breast tomosynthesis is equal to the diagnostic accuracy of digital spot compression, Italian researchers have found. In addition, digital breast tomosynthesis has a lower mean glandular dose and has the potential to help reduce the recall rate.
Mammography benefits from a supplementary view with spot compression over suspicious areas to evaluate microcalcifications, opacities, or architectural distortions, or to identify masses. Digital spot compression view (DSCV) is especially useful when a conventional exam results in an equivocal evaluation of findings other than clustered calcifications. With the advent of digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), 3D cross-sectional visualizations of breast tissue are possible. It has been hypothesized DBT can reduce the recall rate, but that means it must perform as well as or better than DSCV.
According to the hypothesis, a woman with an abnormality requiring DSCV on full-field digital mammography (FFDM) should obtain the same diagnosis as on DBT alone. Dr. Alberto Tagliafico, from the department of experimental medicine at the University of Genoa in Italy, and colleagues compared the two techniques in the same patients to test the hypothesis, and published their findings online first in European Radiology (11 October 2011).
The study included 52 consecutive recalled women without calcification (mean age: 51 ± 12 years) who underwent both DSCV and DBT. The diagnostic accuracy of DBT and DSCV was evaluated by two radiologists of varying experience.
The researchers found that DSCV and DBT both had sensitivities of 100%. However, overall specificity was higher for DBT (100%) than for DSCV (94%). Reader 1 had higher specificity for DSCV (95%) than reader 2 (92%). In addition, reader 1 had two false positives and reader 2 had three false positives for DSCV.
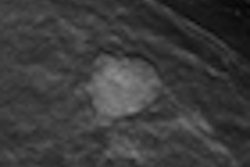
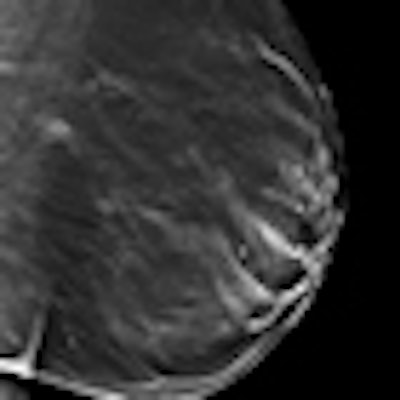
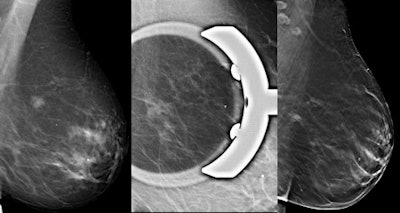 To identify suspicious areas -- for instance, to evaluate microcalcifications -- digital spot compression view is often used as a complement to mammography. Left: Mammography shows a suspicious area first. Center: The same lesion is also visible on digital spot compression. Right: Tomosynthesis gives a better conspicuity of the lesion. All images courtesy of Dr. Alberto Tagliafico.
To identify suspicious areas -- for instance, to evaluate microcalcifications -- digital spot compression view is often used as a complement to mammography. Left: Mammography shows a suspicious area first. Center: The same lesion is also visible on digital spot compression. Right: Tomosynthesis gives a better conspicuity of the lesion. All images courtesy of Dr. Alberto Tagliafico.The researchers also found the area under the curve (AUC) was greater for DBT (AUC = 1) than for DSCV (AUC = 0.963). The mean difference between the two techniques, however, was not significantly different.
The mean glandular dose was 4.69 ± 1.7 mGy for the two projections of FFDM added to DSCV and 2.39 ± 0.6 mGy for DBT.
"The results of this study show that DBT is not inferior to digital spot compression in identifying abnormalities judged as suspicious on FFDM," the researchers wrote. "Moreover, DBT had higher specificity than digital spot compression, showing the potential to reduce the number of biopsies on nonmalignant lesions. Moreover, DBT appeared promising with the potential of improving specificity for the less experienced reader."
DBT had the potential to decrease the recall rate, which may seem counterintuitive because DBT covers the whole breast rather than a specific targeted location, the researchers wrote. However, since DBT has equal sensitivity and better specificity than digital spot compression, the data supports the anecdotal and personal perception of many experts, which suggested that DBT may also have been better than targeted projection such as spot compression.
DBT's ability to outperform DSCV may be inherent in its process. The x-ray tube moving along an arc during the examination acquires a 3D volume of the compressed breast, thus the reconstructed breast volume can be explored by scrolling through the slices, allowing the enhancement of the information contained in each plane while blurring the off-focus information.
A limitation of the study is the relatively short follow-up for the true-negative cases (12 to 16 months) and the relatively small number of patients.
"A strength of this study is that the device used is not a prototype and is commercially available, therefore we believe that our study may be reproduced in daily clinical practice," the researchers wrote.